As temperatures drop, landlords must understand their responsibilities regarding heating in rental properties. The timing of when landlords must turn on the heat is determined by various factors, including local laws and regulations.
In many areas, landlords are required to provide heating during specific months, typically from October to May. Additionally, there are minimum temperature requirements that landlords must adhere to, ensuring tenants have a warm and comfortable living space throughout the colder months.
Can a Landlord Control the Heat?

Yes, landlords can typically control the heat in rental properties. However, the extent of control may vary depending on local regulations and the type of heating system installed. In most cases:
- Landlords are responsible for providing a reliable source of heat and maintaining the heating system in good working condition.
- Landlords may set parameters for temperature control, such as minimum and maximum temperature settings.
- Some rental properties may have individual heating controls for each unit, allowing tenants to adjust the temperature within certain limits.
- Landlords should ensure that heating systems comply with safety regulations and provide adequate warmth during colder months.
Understanding the Legal Requirements
When it comes to renting out properties, understanding the legal requirements is essential. These regulations dictate the responsibilities of both landlords and tenants, ensuring a fair and safe living environment for all parties involved. Let’s delve into the key legal requirements that landlords need to be aware of to maintain compliance and protect their interests.
Can a Tenant Fix the Heating Issue By Themselves?

Tenants can sometimes address minor heating issues on their own, but it depends on the nature of the problem and the terms of the lease agreement. Here’s a breakdown:
Minor Adjustments
Tenants can adjust thermostat settings and ensure that vents and radiators are unobstructed to improve heating efficiency.
Filter Replacement
If the heating system has a filter, tenants may be able to replace it if it’s dirty or clogged, improving airflow and efficiency.
Safety Checks
Tenants can check for obvious issues like tripped circuit breakers or blown fuses and reset them if necessary.
Reporting to Landlord
For more significant issues like malfunctioning furnaces or boilers, tenants should promptly notify the landlord or property management to arrange for professional repairs. Attempting complex repairs without expertise can lead to safety hazards or further damage.
Lease Agreement
Tenants should review the lease agreement to determine if there are specific procedures for reporting and addressing maintenance issues, including heating problems. Some leases may prohibit tenants from making repairs themselves.
The Role of Local And State Laws
Local and state laws play a crucial role in determining the rights and responsibilities of landlords and tenants. These laws outline specific requirements regarding rental properties, including heating provisions. Landlords must familiarize themselves with the laws applicable to their area to ensure they meet legal obligations and avoid potential disputes with tenants. Let’s explore the significance of local and state laws in governing landlord-tenant relationships and heating regulations.
Examining Rental Agreements And Lease Terms
Rental agreements and lease terms are essential documents that outline the rights and responsibilities of both landlords and tenants. These contracts provide clarity on various aspects of the rental arrangement, including heating provisions.
It’s crucial for landlords to carefully examine and understand the terms of these agreements to ensure compliance with legal requirements and avoid misunderstandings with tenants. Let’s delve into the importance of examining rental agreements and lease terms about heating regulations and landlord-tenant relationships.
Navigating Tenant And Landlord Responsibilities
Navigating tenant and landlord responsibilities is vital for maintaining a harmonious rental relationship. Both parties have specific duties outlined by law and rental agreements, including obligations related to heating provisions.
Understanding and fulfilling these responsibilities is essential for ensuring a comfortable and compliant living environment for tenants and protecting the interests of landlords. Let’s explore the roles and duties of both tenants and landlords in navigating heating regulations and maintaining a positive rental experience.
Seasonal Considerations For Heat Provision
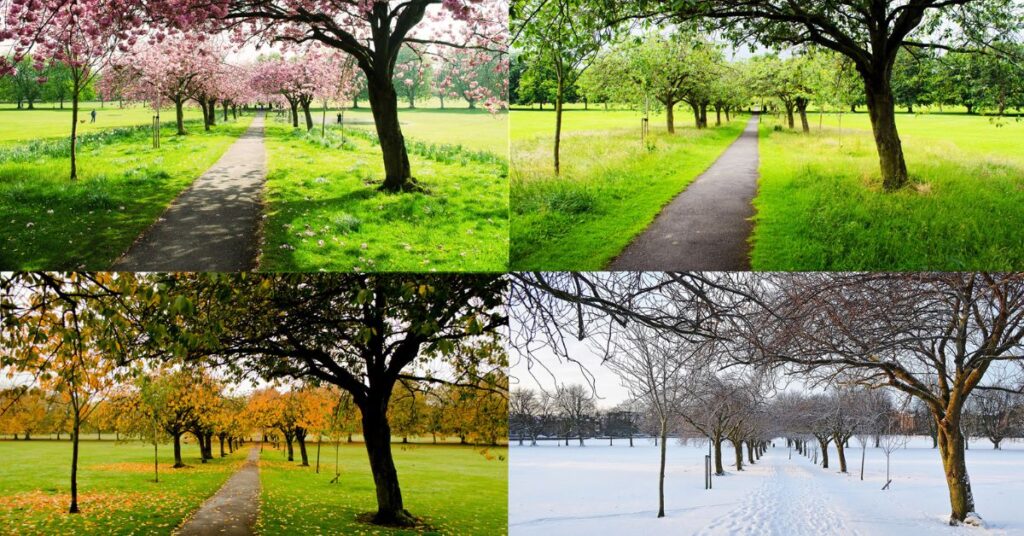

Seasonal considerations for heat provision are crucial for landlords to ensure tenant comfort and safety throughout the year. While heating regulations may vary depending on location, landlords must be mindful of temperature fluctuations during different seasons.
From ensuring adequate heating during colder months to providing proper ventilation in warmer weather, landlords must adapt their heating provisions to meet tenant needs while complying with legal requirements. Let’s explore the seasonal factors landlords should consider when providing heat to rental properties.
Minimum Temperatures To Be Maintained
Maintaining minimum temperatures is a key responsibility for landlords to ensure tenant comfort and well-being. These minimum temperature requirements are often dictated by local laws and regulations, outlining the lowest acceptable temperature for rental properties during different times of the year.
Landlords must adhere to these standards, typically ranging from 68 to 72 degrees Fahrenheit, to provide a habitable living environment for tenants. Let’s delve into the importance of maintaining minimum temperatures in rental properties and the legal implications for landlords.
Timing Of Heat Provision
The timing of heat provision is critical for landlords to consider, ensuring that tenants have access to adequate heating when needed. Landlords should be mindful of when to turn on heating systems, balancing the onset of colder weather with energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
By adhering to guidelines such as starting heating systems in September or when temperatures drop below certain thresholds, landlords can prioritize tenant comfort while fulfilling their legal obligations. Let’s explore the importance of timing in heat provision and how landlords can effectively manage heating schedules in rental properties.
Seasonal Changes In Temperature Control And Requirements
Seasonal changes in temperature control and requirements present landlords with unique challenges in maintaining comfortable living conditions for tenants. As temperatures fluctuate throughout the year, landlords must adjust heating provisions accordingly, ensuring that rental properties remain habitable in both hot and cold weather.
From providing air conditioning during sweltering summers to maintaining minimum temperatures in winter, landlords must adapt their heating and cooling systems to meet seasonal demands while complying with legal standards. Let’s explore the importance of seasonal temperature control and the measures landlords can take to ensure tenant comfort year-round.
Read As: DO I HAVE 30 DAYS TO MOVE AFTER AN EVICTION? PRACTICAL HACKS
During summer
During summer, landlords should prioritize maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures for tenants by ensuring that air conditioning systems are in good working order. It’s essential to provide a cool and pleasant living environment, typically by maintaining indoor temperatures between 74°F and 78°F. Landlords should also ensure proper ventilation and access to fresh air, especially in areas where air conditioning may not be available.
However, landlords can install window screens or provide fans to enhance airflow and improve overall comfort during hot weather. Let’s explore how landlords can effectively manage temperature control in rental properties during the summer months to ensure tenant satisfaction and well-being.
During winter
During winter, landlords must prioritize providing adequate heating to ensure tenant comfort and well-being. This involves maintaining indoor temperatures within a specified range, typically around 68 to 72 degrees Fahrenheit during daytime hours.
Landlords should ensure that heating systems are in good working condition and promptly address any issues or malfunctions to prevent discomfort for tenants. However, proper insulation and sealing of windows and doors can help retain heat and improve energy efficiency in rental properties.
Let’s explore how landlords can effectively manage temperature control in rental properties during the winter months to provide a warm and cozy living environment for tenants.
During spring and fall
During spring and fall, landlords should remain vigilant in maintaining comfortable living conditions for tenants, although heating systems may not be in high demand. It’s essential to conduct periodic inspections and repairs of heating systems, windows, and doors to ensure they are ready for colder temperatures when they return.
While heating may not be necessary during these transitional seasons, landlords should still be prepared to address any unexpected weather changes and provide heating if needed. Additionally, landlords can consider alternative methods of temperature control, such as installing programmable thermostats or providing space heaters for temporary warmth.
Let’s explore how landlords can effectively manage temperature control in rental properties during the spring and fall to ensure tenant comfort and satisfaction throughout the year.
Rental Heating Laws
Rental heating laws outline the responsibilities of landlords in providing and maintaining heating systems in rental properties. These laws vary by state but generally require landlords to ensure that rental units have adequate heating during colder months.
Landlords must comply with safety regulations, provide functional heating systems, and protect tenants from foreseeable hazards related to heating. Additionally, landlords must promptly address any issues or malfunctions with heating systems to ensure tenant comfort and well-being. Let’s explore the key aspects of rental heating laws and how they impact landlords and tenants alike.
Landlord Heating Responsibility
The landlord has a responsibility to ensure that the rental property has a functional heating system. This includes providing access to heat sources such as central heating or other equipment for space heating in every occupied room of the property.
Landlords must also maintain the heating system in good working condition throughout the tenancy to ensure the tenant’s comfort and well-being. Landlords need to understand their heating responsibilities and fulfill them to comply with legal obligations and provide a habitable living environment for tenants.
How Much Time Does a Landlord Have to Fix a Heating Issue?

Landlords typically have a legal obligation to address heating issues promptly to ensure tenant comfort and safety. The specific timeframe for fixing a heating issue may vary depending on the severity of the problem and local regulations.
However, landlords are generally expected to respond to heating complaints within a reasonable amount of time, which could range from a few hours to a few days, depending on the circumstances.
In urgent situations where the lack of heating poses a significant health or safety risk to tenants, such as during extremely cold weather, landlords are expected to act more quickly to resolve the issue. Landlords must communicate with tenants promptly, provide updates on the status of repairs, and take appropriate action to restore heating as soon as possible to comply with legal obligations and maintain tenant satisfaction.
The types of landlord heating issues
| Landlord Heating Issues | Description | Common Causes | Solutions |
| Malfunctioning Furnace/Boiler | Central heating system not functioning properly | Age, lack of maintenance, mechanical issues | Schedule professional inspection and repairs |
| Faulty Thermostat | Inaccurate temperature control or malfunction | Age, wiring issues, sensor problems | Replace thermostat or repair wiring as needed |
| Clogged/Leaky Radiators | Blockages or leaks in the radiator system | Sediment buildup, corrosion, worn seals | Flush radiators, repair leaks, or replace damaged components |
| Insufficient Insulation | Poor heat retention due to inadequate insulation | Aging insulation, gaps, poor installation | Install or upgrade insulation, seal gaps and leaks |
| Pilot Light Issues | Problems with igniting or maintaining the pilot light | Dirty components, faulty thermocouple | Clean or replace components, ensure proper ventilation |
Landlord heating issues can vary in nature and severity, impacting the comfort and safety of tenants. Some common types of heating issues that landlords may encounter include.
Malfunctioning Furnace or Boiler
Problems with the central heating system, such as a malfunctioning furnace or boiler, can lead to inadequate heating or no heat at all in the rental property.
Faulty Thermostat
A faulty thermostat can result in inaccurate temperature readings or difficulty in controlling the heating system, leading to discomfort for tenants.
Clogged or Leaky Radiators
Radiators that are clogged with debris or have leaks can compromise the efficiency of the heating system, resulting in uneven heating or insufficient warmth in certain areas of the property.
Insufficient Insulation
Poor insulation in the rental property can cause heat loss, making it difficult to maintain a comfortable temperature indoors and leading to higher energy bills for both tenants and landlords.
Pilot Light Issues
Gas-powered heating systems may experience pilot light issues, such as a pilot light that keeps going out or fails to ignite, preventing the heating system from functioning properly.
Frequently asked question
When does a landlord have to turn on the heat?
Landlords typically have to provide heat during colder months, often from October to May, depending on local laws. Exact dates and temperature requirements vary by location.
What temperature should the rental property be maintained at?
The minimum temperature for rental units is usually around 68 to 72 degrees Fahrenheit during the day and slightly lower at night, typically 64 degrees Fahrenheit.
Can a landlord charge extra for heat?
No, landlords cannot typically charge extra for heat. The cost of heating should be included in the rent amount.
What if the landlord doesn’t turn on the heat when required?
If the landlord fails to provide heat during the legally required period, tenants can contact their local housing authority for assistance and may have legal remedies available.
What should tenants do if they have heat issues?
Tenants should promptly notify their landlord if there are any issues with heating and document their communication. If the landlord doesn’t respond, they can escalate the issue to local authorities or seek legal advice.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding when landlords must turn on the heat is crucial for both tenants and landlords alike. It’s essential to be aware of the legal requirements outlined by local and state laws, which often mandate specific dates and minimum temperatures for heating provisions. By adhering to these regulations, landlords ensure the comfort and well-being of their tenants during colder months.
However, clear communication between landlords and tenants regarding heating responsibilities is paramount. Both parties should understand their obligations outlined in rental agreements or leases, including timely reporting of any heating issues and prompt resolution by the landlord.
A proactive approach to addressing heating concerns fosters a positive landlord-tenant relationship and ensures compliance with legal standards, promoting a safe and comfortable living environment for all involved.

James, with 5 years of business experience, brings expertise to our website. His profile reflects a commitment to excellence and innovation in his field.